Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
Over the last 20 years, car manufacturers have developed safety features that significantly decrease your chances of getting in an automobile accident and in some cases, saving your life. Some of these new vehicle systems include adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, adaptive light control, blind spot monitoring, and even your backup camera. There are plenty of other A.D.A.S. applications out there as well.
All these different applications make up A.D.A.S. (Advanced Driving Assistance Systems). At least 90% of car accidents are from human error. With more than 1 million people dying in car accidents around the world each year, A.D.A.S. is here to lower that statistic in the years to come. Increased autonomy, increased safety, and overall improved confidence for every single driver out there.
ADAS comes in two different types: passive and active. Passive where the driver is alerted to things such as drifting over into another lane with out a blinker engaged but does not automatically correct itself. Active type is when your vehicle automatically takes action, such as emergency braking or lane correction. The more the driver starts to depend on these ADAS functions, the more important it is to properly calibrate them. Since safety is heavily involved here, liability it is too!
All ADAS components are important. Here’s an example of seemingly small consequences, that in reality are big factors. If the ADAS cameras or radar are off only by half a degree from the manufacturer requirements, which may seem “close enough” in the shop but in reality isn’t close enough. When it comes to braking a vehicle for a pedestrian crossing the street, inches could be the difference between stopping and causing a major accident. That half a degree difference can cause a variance between when your ADAS sees things that aren’t there, or not seeing things that are in fact there.
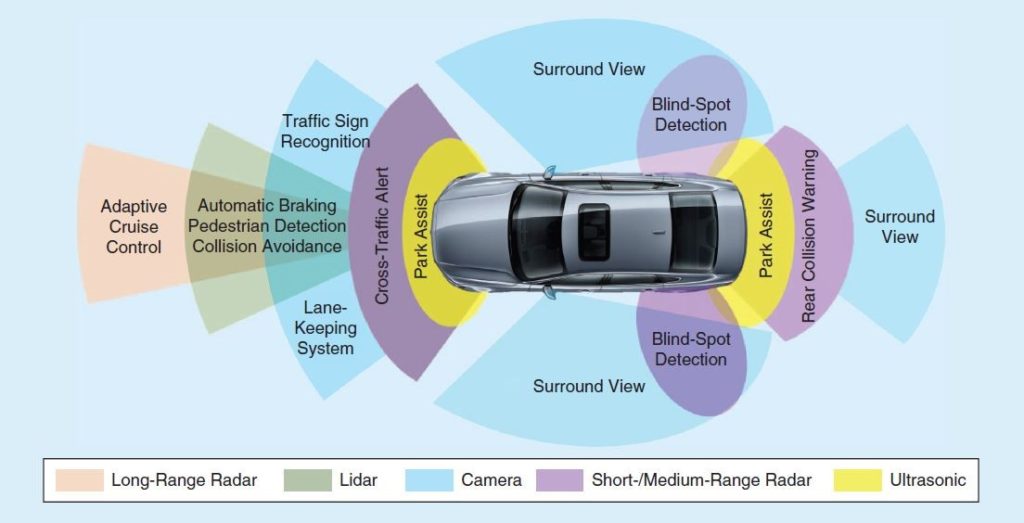

COLLISION WARNING
Blind Spot Monitoring
Detects vehicles in the blind spot while driving, and notifies the driver to their presence. Some systems provide an additional warning if the driver activates the turn signal.
Forward Collision Warning
Detects a potential collision with a vehicle ahead and alerts the driver. Some systems also provide alerts for pedestrians or other objects.
Lane Departure Warning
Monitors vehicle’s position within the driving lane and alerts driver as the vehicle approaches or crosses lane markers.
Parking Collision Warning
Detects objects close to the vehicle during parking maneuvers and notifies the driver.
Rear Cross Traffic Warning
Detects vehicles approaching from the side at the rear of the vehicle while in reverse gear and alerts the driver. Some systems also warn for pedestrians or other objects.
COLLISION INTERVENTION
Automatic Emergency Braking
Detects potential collisions with a vehicle ahead, provides forward collision warning and automatically brakes to avoid a collision or lessen the severity of impact. Some systems also detect pedestrians or other objects.
Automatic Emergency Steering
Detects potential collisions with a vehicle ahead and automatically steers to avoid or lessen the severity of impact. Some systems also detect pedestrians or other objects.
Reverse Automatic Emergency Braking
Detects potential collisions while in reverse gear and automatically brakes to avoid or lessen the severity of impact. Some systems also detect pedestrians or other objects.
DRIVING CONTROL ASSISTANCE
Adaptive Cruise Control
Cruise control that also assists with acceleration and/or braking to maintain a driver-selected gap to the vehicle in front. Some systems can come to a stop and continue while others cannot.
Lane Keeping Assistance
Provide steering support to assist the driver in preventing the vehicle from departing the lane. Some systems also assist to keep the vehicle centered within the lane.
Active Driving Assistance
Provides steering and brake/acceleration support to the driver at the same time. The driver must constantly supervise this support feature and maintain responsibility for driving.
PARKING ASSISTANCE
Backup Camera
Displays the area behind the vehicle when in reverse gear.
Surround View Camera
Displays the immediate surroundings of some or all sides of the vehicle while stopped or during low-speed maneuvers.
Active Parking Assistance
Assists with steering and potentially other functions during parking maneuvers. Driver may be required to accelerate, brake and/or select gear position. Some systems are capable of parallel and/or perpendicular parking. The driver must constantly supervise this support feature and maintain responsibility for parking.
Remote Parking
Without the driver being physically present inside the vehicle, provides steering, braking, accelerating and/or gear selection while moving a vehicle into or out of a parking space. The driver must constantly supervise this support feature and maintain responsibility for parking.
OTHER DRIVER ASSISTANCE SYSTEMS
Automatic High Beams
Switches between high and low beam headlamps automatically based on lighting and traffic
Driver Monitoring
Observes driver actions to estimate if they are not engaged in the task of driving. Some systems may monitor eye movement and/or head position.
Head-Up Display
Projects information relevant to driving into the driver’s forward line of sight.
Night Vision
Improves forward visibility at night by projecting enhanced images on instrument cluster or head-up display.